Compiling OpenMP programs requires special compiler flags to enable parallel directives and link the runtime library. Different compilers use different flags, and understanding compilation options is essential for debugging, optimization, and portability. Proper compilation ensures OpenMP directives are activated and the program can access runtime functions for parallel execution.
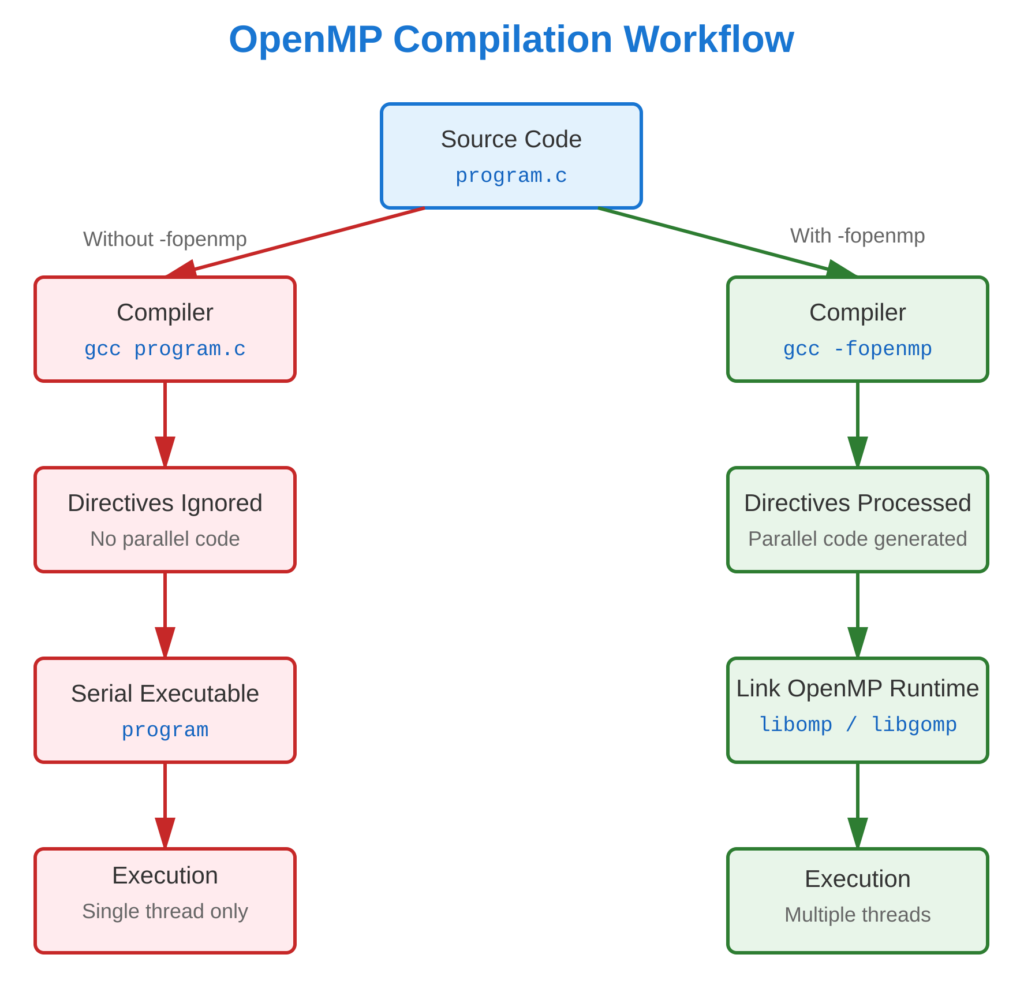
Refer to following diagram for visual overview of compilation workflow.
Core Concept
OpenMP programs require compiler support to process directives and link the runtime library. Without proper flags, OpenMP directives are ignored, and the program runs serially.
GCC (GNU Compiler Collection):
- Flag:
-fopenmp - Example:
gcc -fopenmp -o program program.c
Intel Compiler (icc/icx):
- Flag:
-qopenmp(modern) - Example:
icc -qopenmp -o program program.c
Clang/LLVM:
- Flag:
-fopenmp - May require explicit runtime library linking
- Example:
clang -fopenmp -o program program.c
Compilation Process:
- Preprocessing: Directives are recognized
- Compilation: Parallel code generation
- Linking: Runtime library is linked
- Execution: OpenMP runtime manages threads
Code Example
Compile and run a simple OpenMP program with different compilers and options
Sample Program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <omp.h>
int main() {
#pragma omp parallel
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
printf("Thread %d: Hello!\n", tid);
}
return 0;
}GCC Compilation (Most Common):
# Basic compilation
gcc -fopenmp -o program compile_test.c
# With optimization
gcc -fopenmp -O3 -o program compile_test.c
# With debugging symbols
gcc -fopenmp -g -o program compile_test.c
# With warnings
gcc -fopenmp -Wall -o program compile_test.cIntel Compiler:
icc -qopenmp -o program compile_test.cClang Compiler:
clang -fopenmp -o program compile_test.cExecution:
# Default execution
./program
# Set thread count via environment variable
OMP_NUM_THREADS=4 ./program
# Run with specific configuration
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=8
export OMP_PROC_BIND=close
./programVerification (Without OpenMP flag):
# Compile WITHOUT -fopenmp (directives ignored)
gcc -o program_serial compile_test.c
# Will print only one thread (serial execution)
./program_serialCommon Compilation Errors:
- Missing
-fopenmp: Directives ignored, runs serially - Undefined reference to
omp_*: Runtime library not linked - Header not found: Need
#include <omp.h>
Usage & Best Practices
When to Use Different Options
- Development: Use
-fopenmp -g -Wallfor debugging and warnings - Production: Use
-fopenmp -O3for optimized performance - Testing: Compile both with and without
-fopenmpto verify parallelization - Debugging: Use
-gfor GDB debugging,-fsanitize=threadfor race detection
Best Practices
- Always verify OpenMP is enabled by checking thread count output
- Use optimization flags (
-O2or-O3) for performance measurements - Keep debug and release builds separate
- Use Makefiles for reproducible builds
- Test with different compilers when possible for portability
Common Mistakes
- Avoid: Forgetting
-fopenmpflag (program runs serially without errors) - Avoid: Mixing different OpenMP implementations in linked libraries
Key Takeaways
Summary:
- OpenMP requires compiler support via flags:
-fopenmp(GCC/Clang) or-qopenmp(Intel) - Without proper flags, OpenMP directives are ignored and programs run serially
- Compilation combines preprocessing, compilation, and linking of runtime library
- Different optimization and debugging options affect performance and development workflow
- Always verify OpenMP is active by checking actual thread execution
Quick Reference
Compilation Commands:
# GCC (most common)
gcc -fopenmp -o program source.c
# With optimization
gcc -fopenmp -O3 -o program source.c
# With debugging
gcc -fopenmp -g -o program source.c