Writing your first parallel region in OpenMP is a good starting point. The “Hello Parallel World” program shows how multiple threads run at the same time, each with its own unique identity. This example teaches you how to create threads, identify them, and understand that their order of execution can be unpredictable. Understanding these basics is important before moving on to more complex parallel patterns and data sharing.
Refer to following diagram for parallel execution visualization
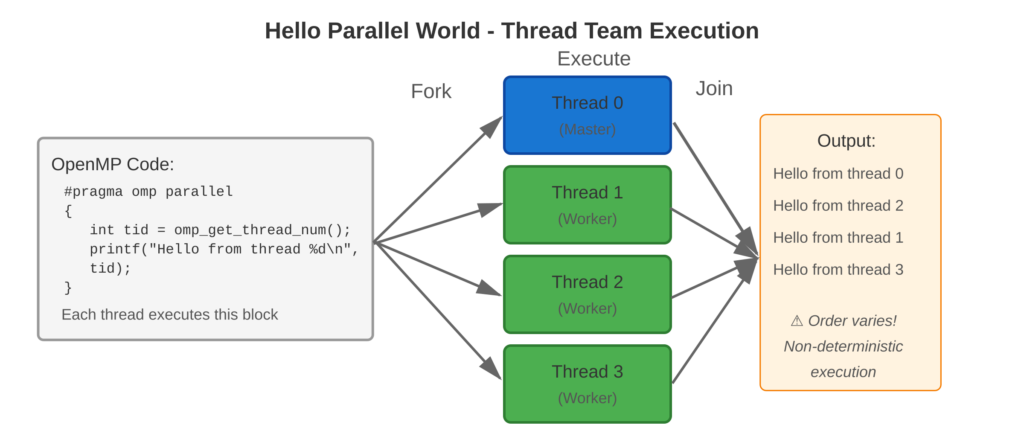
Core Concept
The #pragma omp parallel command creates a group of threads. Each thread runs all the code inside the parallel region by itself. Threads can access their unique IDs (like 0, 1, 2, …, N-1) using omp_get_thread_num(). Thread 0 is called the master thread. The order in which threads print output is random because it depends on how the operating system schedule them.
Key Points
- Parallel Directive:
#pragma omp parallelmarks code for concurrent execution - Thread Team: All threads execute the same code block
- Thread ID: Each thread has a unique identifier from 0 to N-1
- Master Thread: Thread 0 is special—it existed before the parallel region
- Non-Deterministic Order: Thread execution order varies between runs
- Implicit Join: Threads synchronize at the end of the parallel region
Code Example
First parallel region printing messages from each thread
OpenMP Implementation:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <omp.h>
int main() {
int total_threads;
// Serial region
printf("Starting parallel hello world program\n\n");
// Parallel region starts here
#pragma omp parallel
{
int thread_id = omp_get_thread_num();
int num_threads = omp_get_num_threads();
printf("Hello from thread %d of %d threads!\n",
thread_id, num_threads);
// Only master thread executes this
if (thread_id == 0) {
total_threads = num_threads;
printf(" [Master thread reporting: %d threads created]\n",
total_threads);
}
}
// Parallel region ends, implicit barrier and join
printf("\nAll threads finished. Back to serial execution.\n");
return 0;
}Expected Output (4 threads):
Starting parallel hello world program
Hello from thread 0 of 4 threads!
[Master thread reporting: 4 threads created]
Hello from thread 2 of 4 threads!
Hello from thread 1 of 4 threads!
Hello from thread 3 of 4 threads!
All threads finished. Back to serial execution.Note: Thread output order varies between runs.
Usage & Best Practices
When to Use
- Learning parallel execution fundamentals
- Testing OpenMP installation and compilation
- Debugging thread creation issues
- Understanding non-deterministic parallel behavior
Best Practices
- Always include
<omp.h>for runtime functions - Use thread ID conditionals for thread-specific operations
- Understand that printf is not thread-safe (output may interleave)
- Test with various thread counts (set via
OMP_NUM_THREADS) - Verify parallel execution (check that multiple thread IDs appear)
Common Mistakes
- Forgetting
-fopenmpflag produces serial execution - Assuming deterministic output order
Key Takeaways
Summary:
#pragma omp parallelcreates concurrent thread teams- Each thread has unique ID accessible via
omp_get_thread_num() - All threads execute the same code block independently
- Thread execution order is non-deterministic
- Master thread (ID 0) persists throughout program execution
Quick Reference
Basic Parallel Region:
#pragma omp parallel
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
// Code executed by all threads
}Compilation:
gcc -fopenmp -o hello hello_parallel.c
OMP_NUM_THREADS=4 ./hello